Algorithm, Interface & Backends#
Overview#
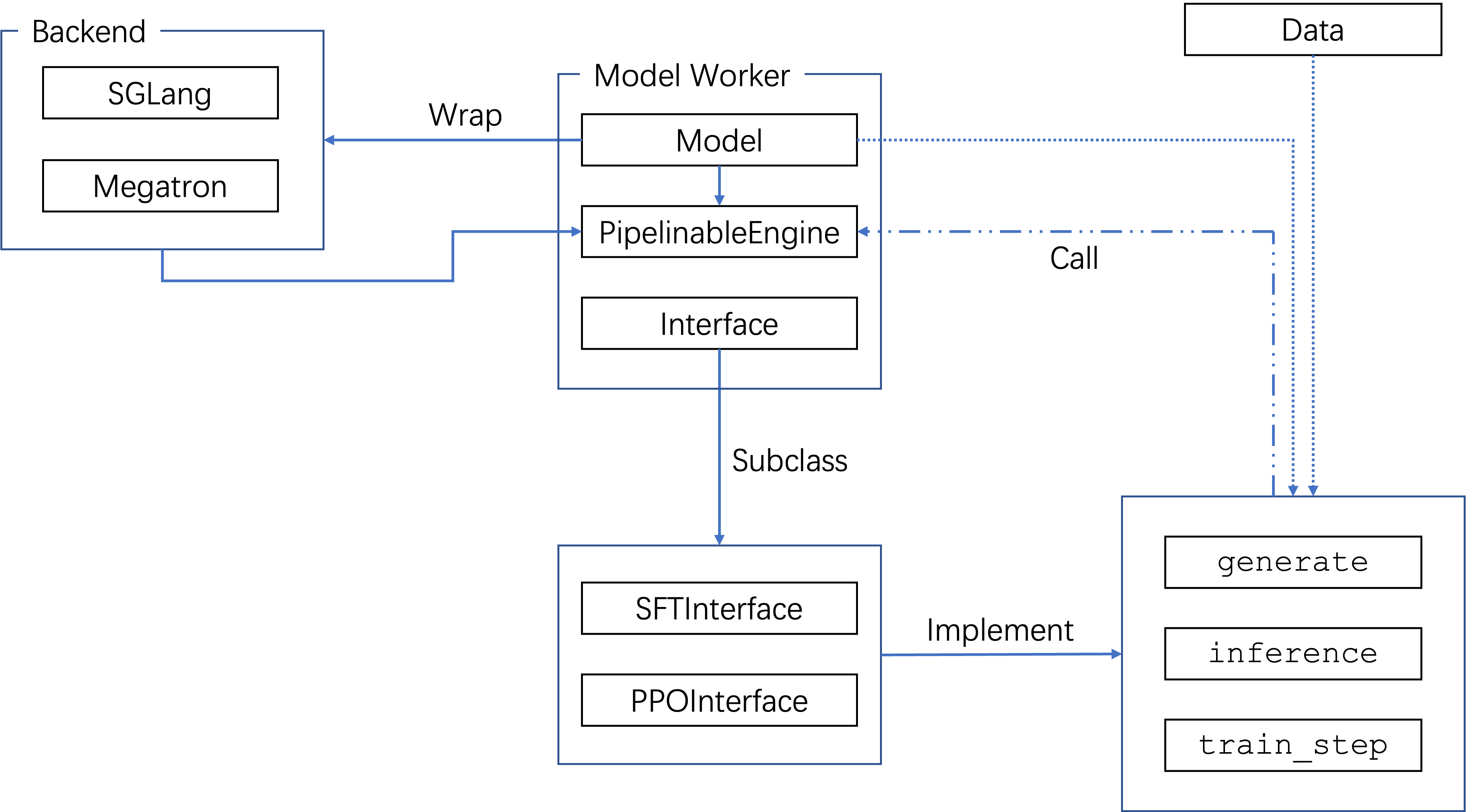
Model Interfaces define the computations that can be performed, such as training, inference, and generation. They provide abstract classes and implementations that decouple specific algorithms (e.g., PPO, SFT) from model backends (Megatron, SGLang, vLLM). Algorithm developpers may be more interested in adding customized model interfaces.
Model backends integrate external libraries to wrap over the model as a
PipelinableEngine, such that they can provide efficient distributed training and
inference capabilities.
Registeration#
Backends and interfaces have similar registeration protocols:
# Registration (at the end of each interface implementation):
model_api.register_interface("ppo", PPOActorInterface)
# Configuration (in experiment config file):
interface_config = ModelInterfaceAbstraction(
type_="ppo",
args=dict(eps_clip=0.2)
)
# Instantiation (in model worker):
interface = make_interface(interface_config)
Customization#
Interfaces#
An interface implementation essentially processes the data and loss function (e.g.,
reward clipping, computing GAEs) required by a PipelinableEngine, calls the actual
execution method such as PipelinableEngine.train_step, and then runs some
post-processing according to the data protocol.
Custom interfaces can be created by subclassing the ModelInterface class and
implementing the required methods for the desired training paradigm.
Example:
@dataclass
class CustomInterface(model_api.ModelInterface):
# Custom parameters
custom_param: float = 1.0
def train_step(self, model, data, mb_spec):
module = model.module
module.train()
# Custom training logic
stats = module.train_batch(
input_=data,
loss_fn=custom_loss_function,
loss_weight_fn=lambda x: x.data["mask"].count_nonzero(),
token_normalize_scope="global",
mb_spec=mb_spec,
version_steps=model.version.global_step,
)
model.inc_version()
return stats
def save(self, model, save_dir):
module = model.module
module.save_to_hf(tokenizer=model.tokenizer, save_dir=save_dir)
# Register the interface
model_api.register_interface("custom", CustomInterface)
Required methods vary based on the interface purpose:
For training interfaces:
train_step()andsave()For inference-only interfaces:
inference()For generation interfaces:
generate()
The interface can be configured in the experiment configuration file, e.g.,
ppo_math_exp.py. Please refer to xxx how to run unittests on your implementation.
Backends#
Backend requires implementing the _initializemethod. Example:
class FSDPEngine(PipelinableEngine):
def train_step(self, ...):
...
class FSDPBackend(ModelBackend):
def _initialize(self, model):
module = model.module
model.module: PipelinableEngine = FSDPEngine(module)
return model
register_backend("fsdp", FSDPBackend)
Existing Implementations#
Interfaces#
ppo_interface.py: Implemetation of PPO actor and critic.sft_interface.py: Implementation of SFT.
Backends#
megatron.py: Training wrapper based on Megatron Core’sDistributedDataParallelsglang.py: A wrapper over a SGLang HTTP server for batched generation.vllm.py: Deprecated SPMD vLLM backend.
