Generation Server and Manager#
Server#
The GenerationServer launches an SGLang subprocess during setup and writes the
server’s address to name_resolve so that other workers can discover it. It serves as a
thin wrapper over SGLang’s launch_server command.
Request scheduling and parameter versioning across different servers are managed by the
GserverManager, which we’ll introduce in the next section.
Manager#
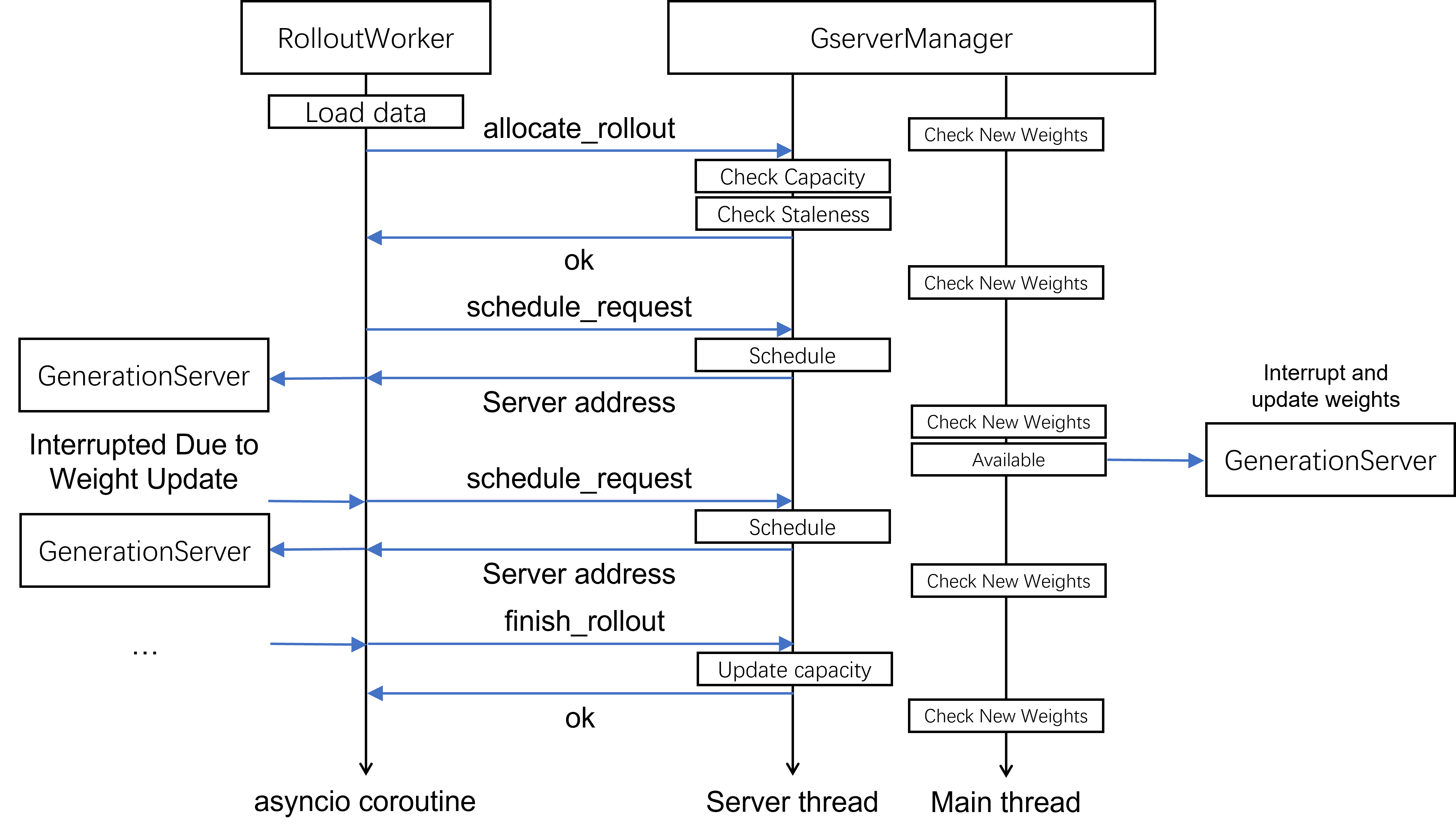
Server Thread#
The GserverManager launches a fastapi server thread for rollout workers to invoke.
There are three main types of APIs:
allocate_request: The manager decides whether to allow submission of a new rollout request based on capacity and data staleness
schedule_request: The manager routes initial or interrupted requests to a generation server address
finish_rollout: The manager releases the slot and allows allocation of new rollouts
Since the generation of each trajectory must pass through the centralized manager, we
can conveniently control data staleness. For details on staleness control, refer to the
is_staled method of GserverManager.
Main Thread#
The main thread of GserverManager executes the _poll method, which primarily checks
whether new weights are available. When new weights are detected, it sends update weight
requests to all generation servers to interrupt ongoing requests and update the weights
to the latest version.
