AEnvironment#
Everything as Environment — A production-grade environment platform for Agentic Reinforcement Learning.
What is AEnvironment?#
AEnvironment (AEnv) is a unified environment platform designed for the Agentic RL era. It provides a complete solution for:
🎯 Model Benchmarking: Built-in support for popular benchmarks (TAU, SWE-bench, etc.)
🚀 RL Training at Scale: Seamless integration with RL frameworks (AReaL, VERL, SLIME)
🤖 Agent Development: Rich tooling for building and testing AI agents
🔧 Custom Environments: Easy-to-use SDK for creating new environments
Design Philosophy#
Everything as Environment#
AEnvironment treats everything as an environment — from simple tools to complex multi-agent systems. This unified abstraction enables:
graph LR
A[Agent] --> B[Environment]
B --> C[Tools]
B --> D[Other Agents]
B --> E[Benchmarks]
B --> F[Real Services]
Composability: Environments can be nested and composed
Interoperability: Standard MCP protocol for tool communication
Scalability: From local development to distributed clusters
Agent as Environment#
A unique feature of AEnvironment is treating agents themselves as environments. This enables:
A2A (Agent-to-Agent): Agents can interact with other agents as environments
Multi-Agent Systems: Build complex agent ecosystems
Agent Testing: Use agents to test other agents
Key Features#
Built-in support for mainstream benchmarks. Get started with SWE-bench, TAU, and more in minutes.
Optimized runtime delivers fast environment creation compared to traditional container solutions.
Full compatibility with Model Context Protocol for seamless tool integration.
From code to running environment in 30 seconds with our SDK and CLI tools.
Native support for OpenAI Agents, CAMEL, and other popular agent frameworks.
Battle-tested infrastructure powering Ant Group’s AI applications.
Quick Example#
from aenv import Environment, register_tool
# Define a tool
@register_tool
def search_code(query: str, max_results: int = 10) -> list:
"""Search code in the repository."""
return [{"file": "main.py", "line": 42, "content": "..."}]
# Use the environment
async with Environment("swe-env") as env:
# List available tools
tools = await env.list_tools()
# Call a tool
result = await env.call_tool("search_code", {"query": "bug fix"})
print(result.content)
Architecture Overview#
AEnvironment adopts a layered architecture design, dividing the system into two core domains: the Development Side and the Traffic Side, achieving decoupling between environment development and runtime execution.
Core Characteristics#
Architecture Design: Development side defines environments, traffic side executes runtime, providing unified interfaces based on MCP protocol
Extensibility: Supports extensible sandbox engines such as Kubernetes
Metadata-Driven: Environment configurations are stored in EnvHub, queried dynamically at runtime, supporting environment version management and rapid iteration
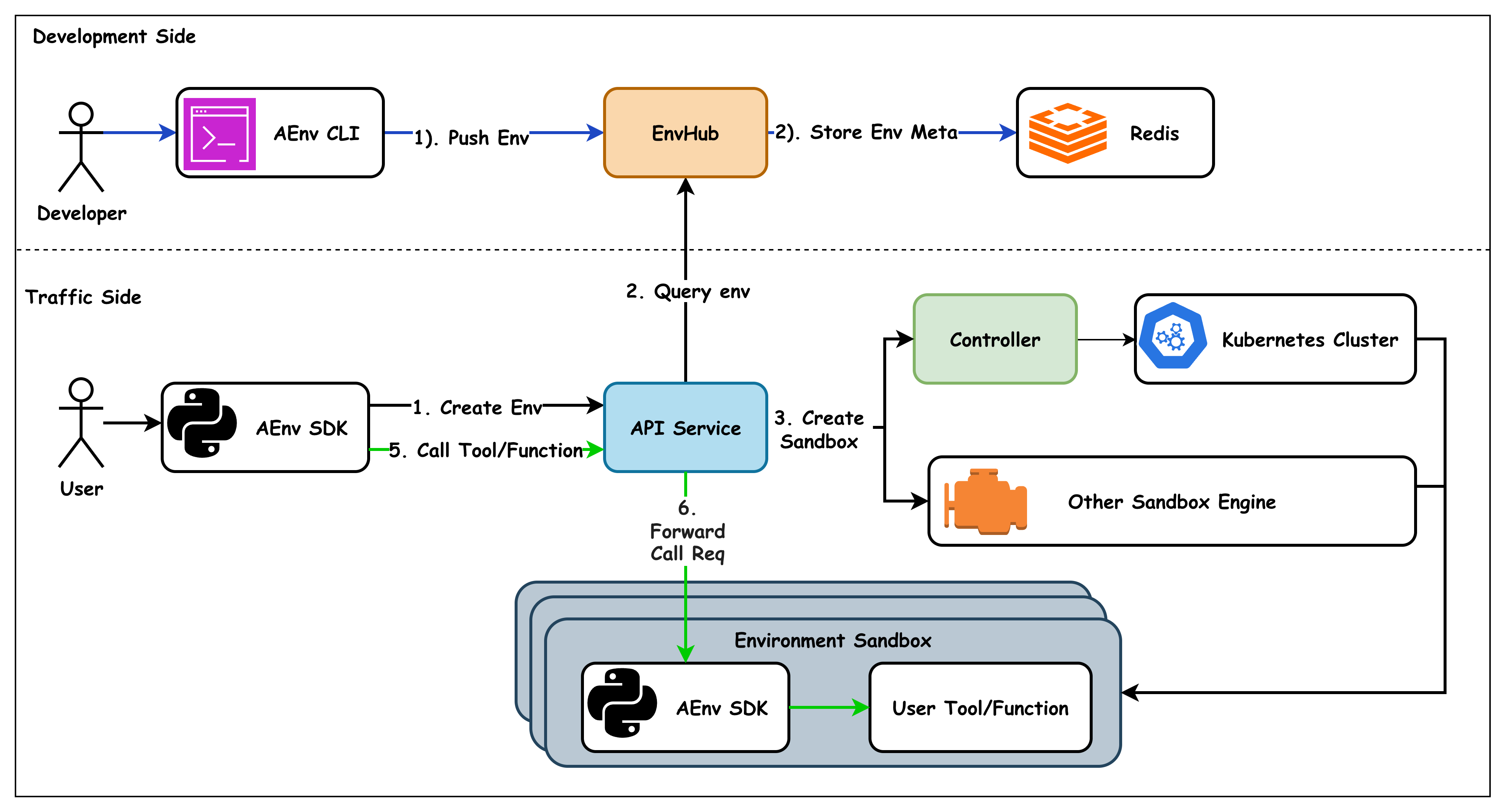
Development Side#
Responsible for environment definition and metadata management:
Flow: AEnv CLI → EnvHub → Redis
Developers push environment configurations to EnvHub through CLI, with metadata stored in Redis
Traffic Side#
Responsible for creating and managing runtime environment instances:
Flow: AEnv SDK → API Service → Controller/Other Sandbox Engine → Environment Sandbox
Users create environment instances through SDK, API Service queries EnvHub for metadata, and creates instances through sandbox engines (e.g., Kubernetes)
Tool invocations are proxied by API Service to SDK within the sandbox, executing MCP tools and returning results
Getting Started#
Ready to dive in? Check out our Quick Start Guide guide to create your first environment in minutes.
Getting Started
Architecture
Examples
Roadmap
Development
